According to a recent ITIC report, the cost of one minute of per server downtime ranges from $1,670 per server, per minute for an hourly outage cost of $100,000, to $16,700 per server per minute for an hourly outage cost estimated at one million dollars ($1,000,000).
The report emphasizes that even a small business that estimates the cost of downtime at a modest $10,000 an hour, will rack up outage fees of $167 per minute for a single server.
Today, more than ever, server uptime is crucial for any business to operate smoothly. Let’s take a look at what server uptime is and why it is so important to digital organizations.
What Is Server Uptime?
Uptime refers to the time a system runs without a shutdown or restart. Server uptime is the total duration for which a server is fully functional and running. It is a metric used to denote the performance of a server. Server uptime is monitored and measured by server monitoring tools.
What Is the Difference Between Uptime and Availability?
Uptime and availability are quite often used interchangeably even though they are not the same thing. Uptime is the amount of time a server works properly and is expressed in years, months, days, hours, minutes and seconds. However, availability is the percentage of time, in a specific time interval, during which a server can be used for its intended purpose.
In mathematical terms, Availability % = Uptime/Total time (Total time = Uptime + Downtime).
What Is a Good Server Availability Percentage?
When a company’s IT department or managed service provider (MSP) provides IT services either to the business or to its clients, it often commits to meeting what is known as a service-level agreement (SLA). The SLA defines what the end users should expect in terms of things like system availability, among other details of service delivery. An SLA is important for a service provider to drive its internal processes by setting clear and measurable performance standards.
A server availability SLA specifies the maximum amount of downtime a server can undergo during a certain period of time, such as a year, for example. While achieving 100% percent availability may not be possible, a target of four or five nines (99.99% or 99.999%) of server availability could be a reasonable goal.
According to TechTarget:
- Five nines or 99.999% availability amounts to to 5 minutes and 15 seconds or less of downtime in a year.
- Four nines or 99.99% availability amounts to 52 minutes and 36 seconds downtime per year.
- Three nines or 99.9% availability amounts to 8 hours and 46 minutes downtime per year.
- Two nines or 99% availability amounts to 3 days, 15 hours and 40 minutes downtime per year.
What Is a High-Availability Server?
When a server is capable of remaining available and functional for a very high percentage of time, it is called a high-availability server. This type of server is typically used for business-critical applications in an organization.
A server with 99.999 percent availability, which translates to approximately 5 minutes of downtime a year, is considered to be a high-availability server. The ITIC 2020 report mentioned previously says “… 87% of respondents consider 99.99% — which equals to 52.56 minutes of unplanned per server/per annum downtime — to be the minimum acceptable level of availability for mission-critical servers and applications.”
What Is Server Maintenance?
Server maintenance is the process of keeping a server updated and running at peak performance. Servers are the backbone of IT infrastructure in any company, with crucial processes depending on it. Server maintenance ensures all servers work at their optimum level and are free of security risks. A few common server maintenance tasks should be performed periodically:
- Keep the operating system (OS) up to date
- Check disk usage and stay under 90% of disk capacity
- Check server utilization (e.g., CPU, RAM, and network utilization)
- Check logs for hardware errors
- Verify backups working properly
Server Uptime Monitoring
Server health can be optimized by monitoring server uptime. Monitoring helps minimize costly downtime with alerts and reports.
How Can I Check Server Uptime?
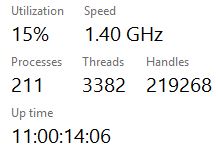
Windows device uptime can be checked using the Task Manager:
- Right-click the Windows taskbar and select Task Manager
- Once Task Manager is open, click the Performance tab. Under the Performance tab, you will find the label Uptime.
You can also see the last boot time for Windows machines from the command prompt by typing:
> systeminfo
You’ll see something like this in the output:

For Linux servers, uptime can be checked remotely by opening the terminal window and then typing the “uptime” command.
Server Monitoring Tools
Server monitoring tools monitor the performance of the system by tracking CPU usage, memory consumption, disk usage and more. These tools enable IT teams to monitor and identify performance-related issues and perform routine maintenance to optimize server uptime.
Kaseya VSA, an endpoint and network monitoring and management solution, monitors all aspects of network-connected devices, including servers, desktops, laptops, hypervisors, routers, switches, firewalls and more.
Kaseya VSA’s server management capabilities enable IT professionals to proactively monitor all servers — including physical and virtual servers — to see real-time information in order to maintain server availability and keep the business running smoothly.
Learn more about Kaseya VSA.


