“The most valuable characteristic of BMS is its balanced ease of use with functionality. My quarter-century experience with PSA solutions gave me the opportunity to fumble with everything from home-grown code to TigerPaw to Connectwise Manager. Far superior to the others, I find Kaseya’s BMS to be the rightmost combination of integration and friendliness.”
Modernize your MSP Business and Get Ahead of the Game
Whopping 65% YOY Growth - The Fastest Growing PSA
END-TO-END NEXT-GEN SOLUTION
Everything you need to delight your customers
Run your entire business, from ticketing, project management, quoting to billing, and more, all in a modern and intuitive platform.
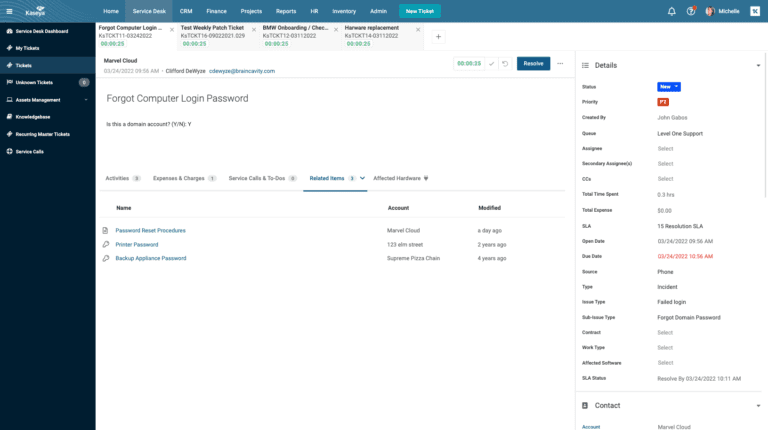
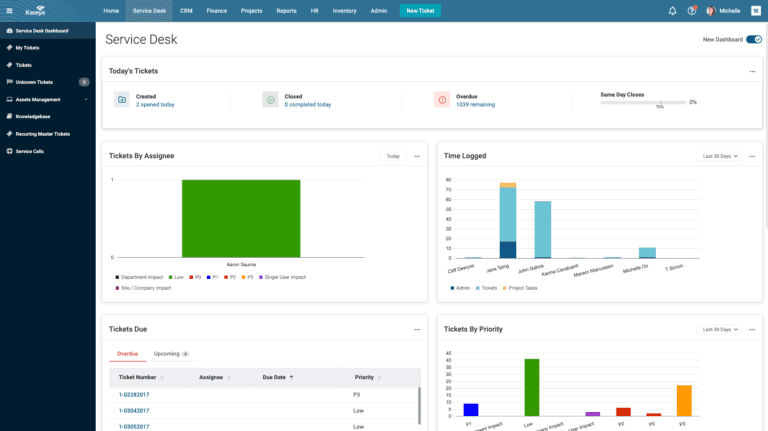
DOCUMENTATION-FIRST SERVICE DESK
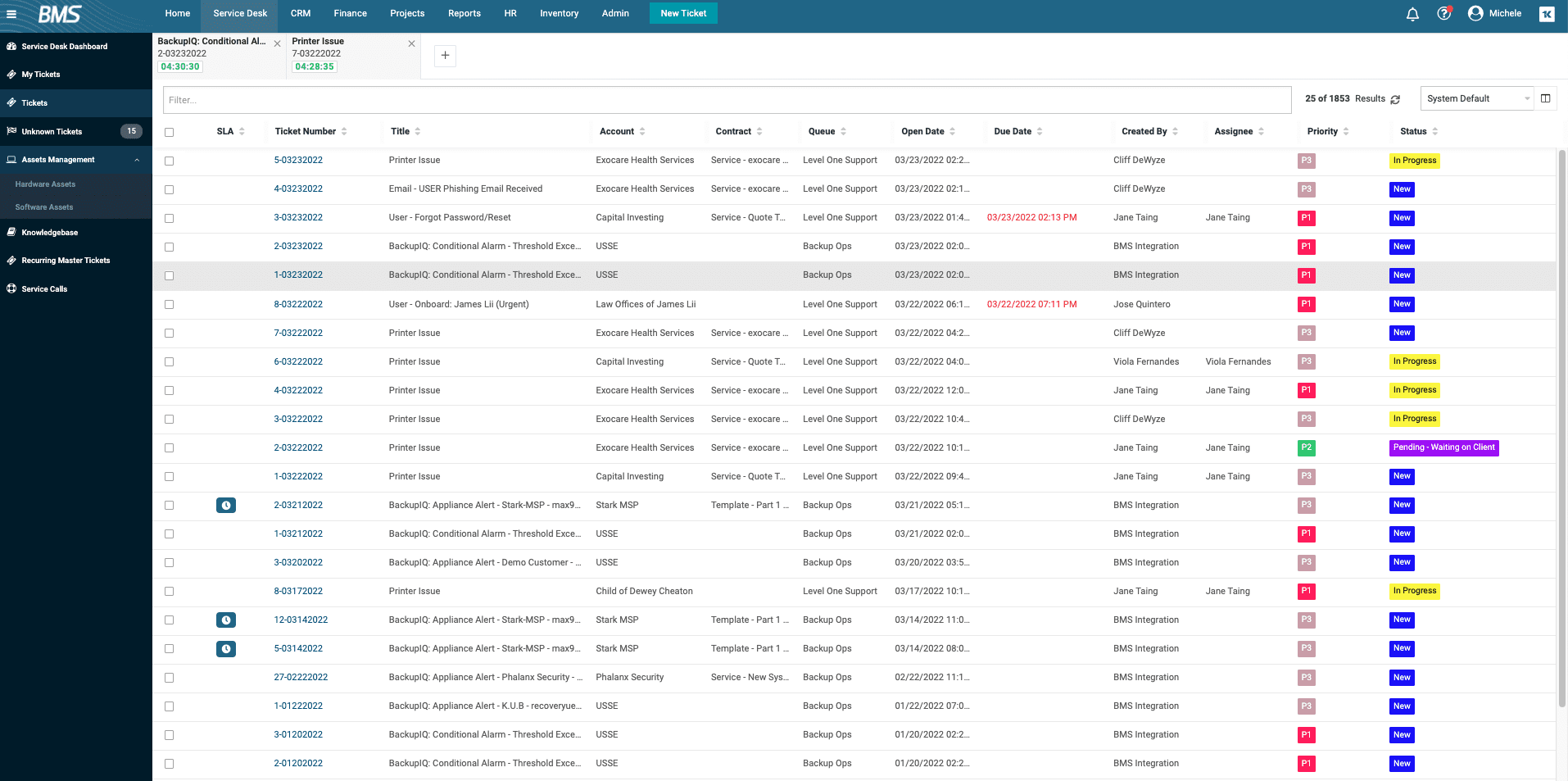
Crush tickets with information at your fingertips
PSA-integrated documentation increases tech momentum by 25% for accurate and faster resolution of each and every ticket.
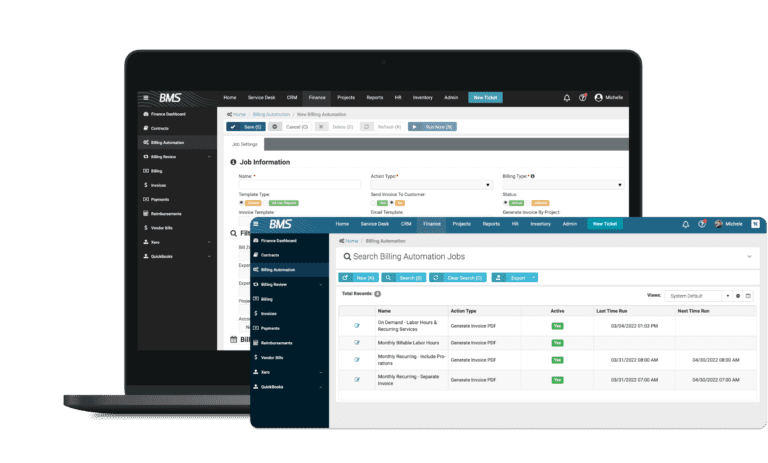
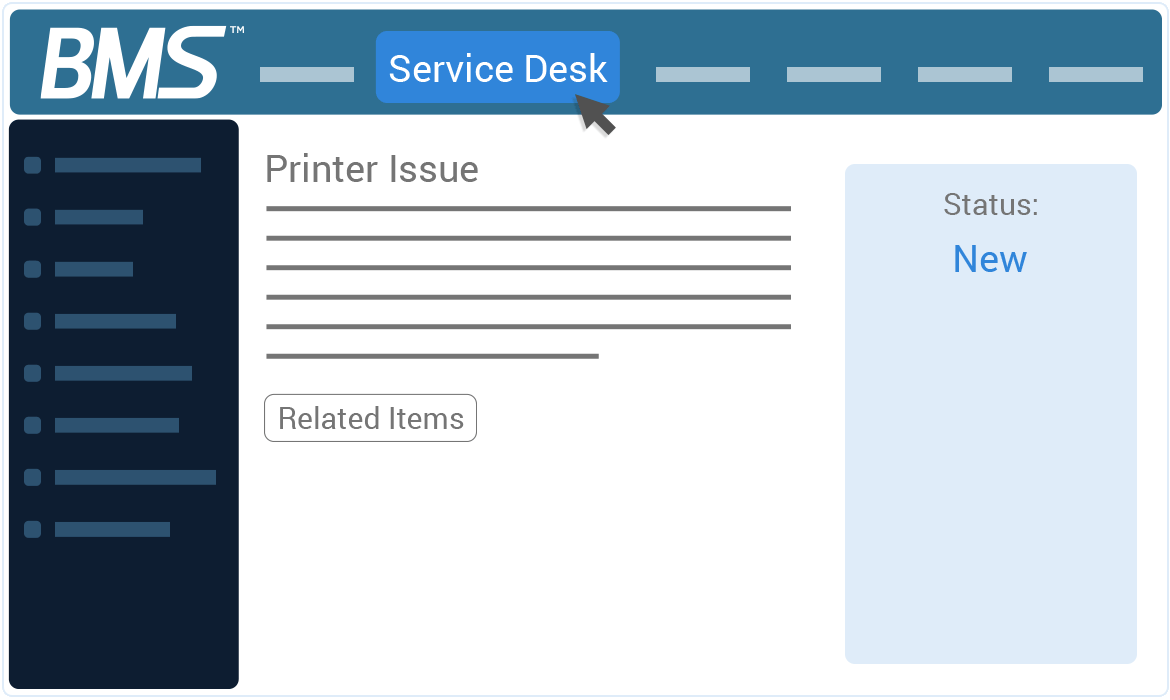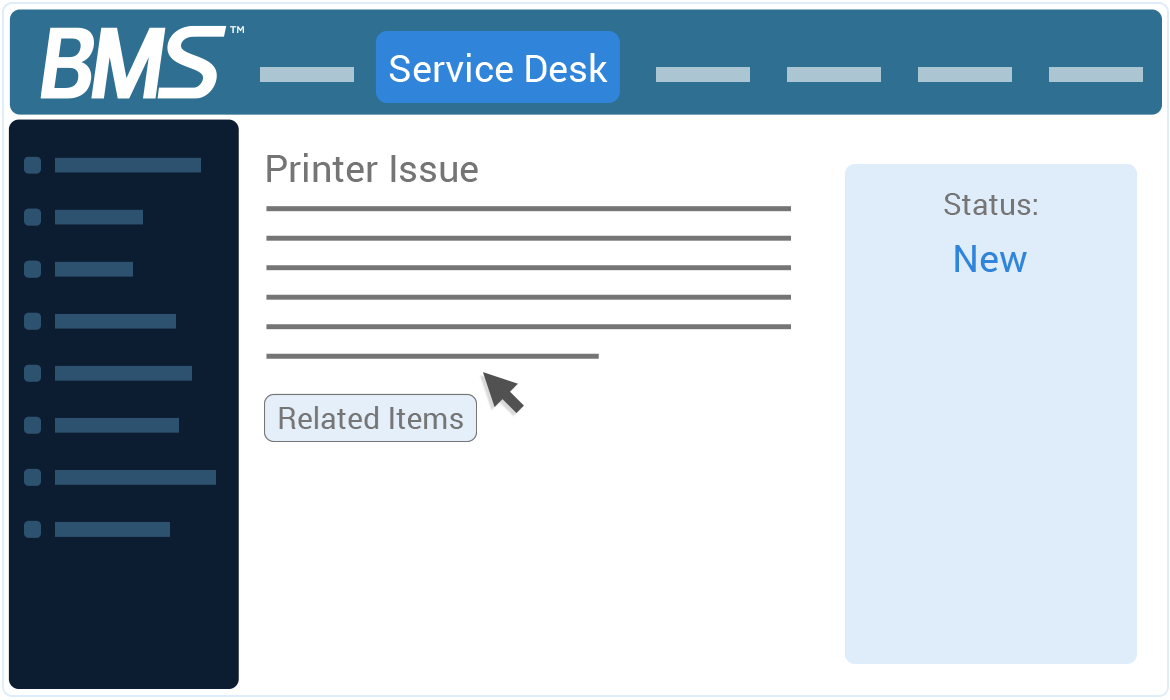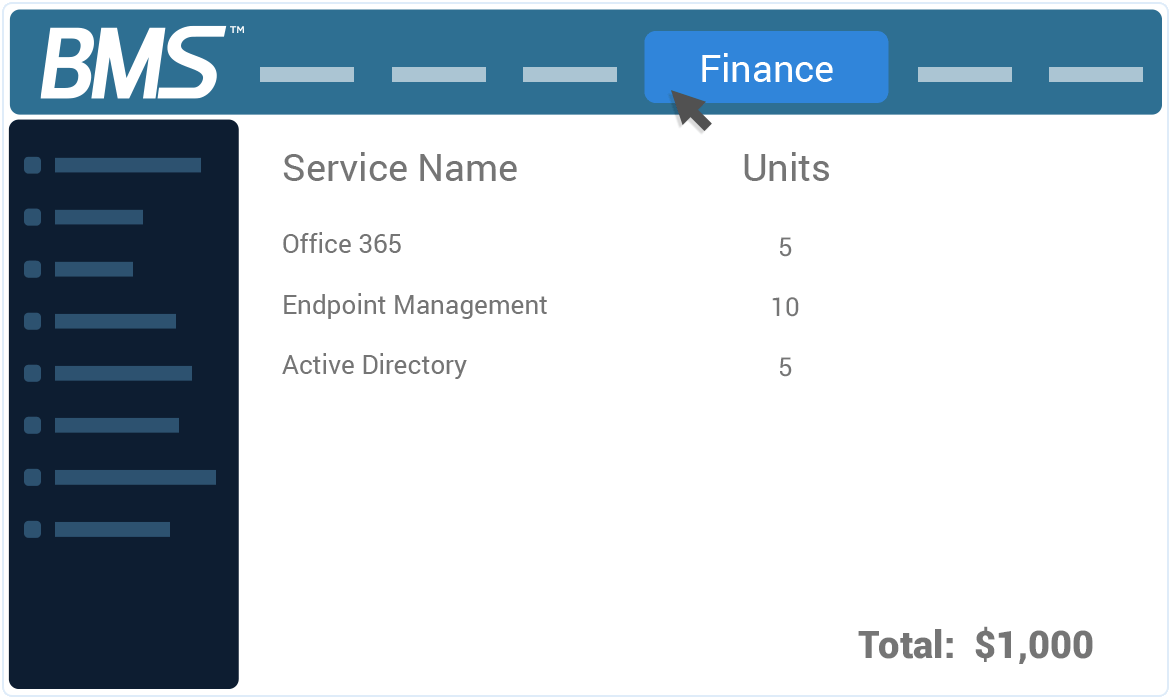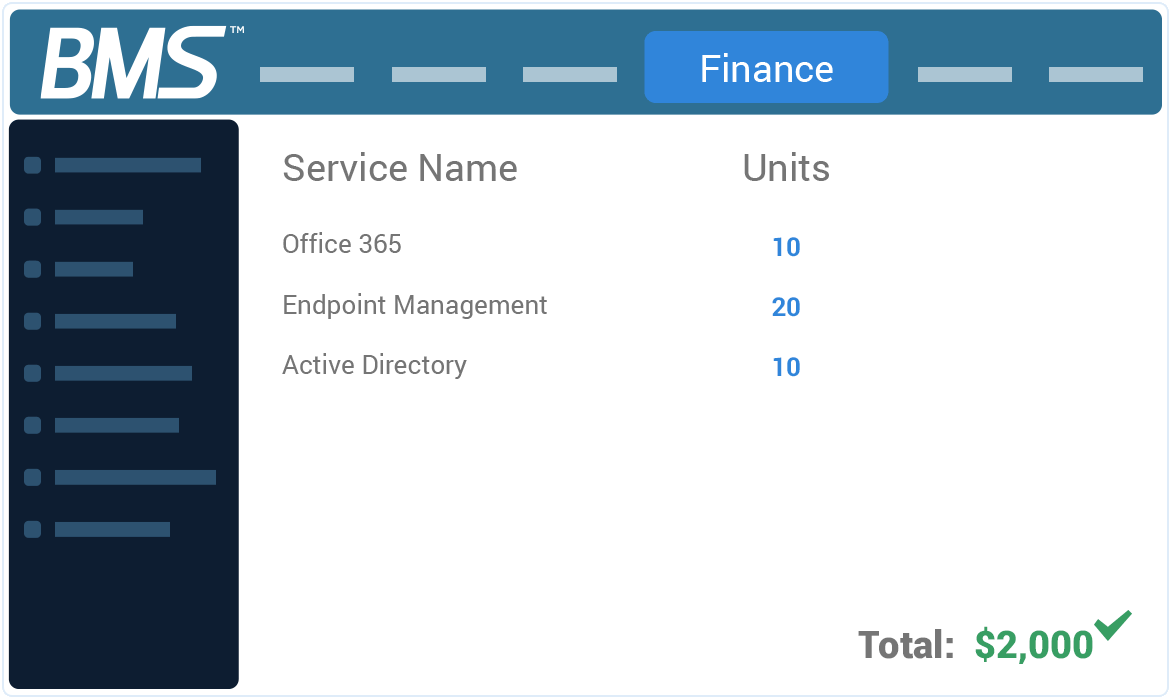
FLAWLESS BILLING
Eradicate billing errors & inefficiencies completely
BMS eliminates human error with end-to-end billing automation for accurate and timely invoices every single time.
“The initial migration from Connectwise Manager was not only fast and simplistic, it gave us the opportunity to clean out years of sludge and replace bad habits with quality processes. The continuous improvement, most recently in the form of the updated user interface, ensures it will retain relevancy as our industry evolves. I’m grateful to have this rightmost solution as the center of our operations.”
James Sanders
Shared Resources Technology Solutions
Switching to BMS?
Years of data stuck in an inefficient and costly PSA? No sweat! Get set up, onboarded, and trained fuss-free with BMS Migrate.
Connect with the tools you already use
Don’t just take our word for it.
See what Next-Gen MSPs say about BMS.
Frequently Asked Questions:
An individual or an organization provides professional services to customers to help improve their business functions and drive growth. Professional services do not involve the physical sale of products, but rather the application of a specific skill in which the provider has specialized training and, in some cases, a license to practice. These services involve delivering non-physical products such as accounting, legal, marketing, consulting, recruiting, event management and IT services.
In the context of IT, professional services include providing IT infrastructure management to clients as those provided by managed service providers (MSPs). MSPs evaluate the needs of their clients and design the best IT infrastructure setup for them. They also oversee the daily management of the IT environment and provide consultation for the best tools, solutions and courses of action for a fee.
Professional services automation refers to using cutting-edge solutions, like professional services automation software, to automate repetitive tasks, streamline service delivery, improve business efficiency, lower overhead costs and increase profitability. It also involves consolidating fragmented data and processes within a single platform to achieve seamless automated workflows and leveraging the data and insights provided by the tool to make better business decisions.
Companies that charge by the billable hour or follow a subscription billing model greatly benefit from professional services automation. Without the help of a PSA tool, professional service providers lose precious hours keeping track of these details and end up leaving a lot of money on the table. By automating and streamlining these business processes that are hard to track manually, PSA tools help organizations optimize revenue and reduce costs, ensuring maximum profitability.
Modern PSA software integrates all the administrative and operational functions into a single platform and helps MSPs streamline their business processes, making them more efficient and profitable. The solution also removes barriers arising from using fragmented tools and empowers MSPs to run their IT operations confidently and efficiently. With the pressure and monotony of daily, mundane tasks lifted, MSPs can work on growth initiatives with greater vigor and confidence. Some of the processes that can be automated and managed using a PSA tool are:
- Ticketing
- Quoting
- Billing
- Invoicing
- Project management
- Time and expense tracking
A PSA tool breaks down the information silos and barriers that come with working with disparate, disjointed tools. The system centralizes project details and data in one location, creating transparency at work, which allows employees to reduce errors and solve problems in real time. In addition, a PSA tool also enables employees from almost all departments to automate repetitive tasks, which helps to save time.
The ability to gather all of the important data in one tool allows employees and managers to better plan, manage and measure the success of various projects. Additionally, it allows businesses to channel more resources toward more profitable projects and eliminate the ones that are unprofitable.
PSA is a key solution for MSP businesses. Armed with the right PSA solution, you can help your team work more efficiently and manage your entire customer journey more effectively. A cutting-edge PSA software, like BMS by Kaseya, has helped thousands of MSPs enhance service delivery, meet SLAs, improve customer experience and minimize administrative costs. BMS also provides real-time data insights for better decision-making so you can constantly keep improving your business process.
MSPs use PSA software to streamline their internal business processes and workflows so they can provide seamless and superior service to their clients. A PSA solution can also help small and midsize businesses (SMBs) replace fragmented tools, achieve IT process flexibility and agility, identify cost leaks and improve their IT infrastructure. A PSA tool breaks down communication silos between departments and personnel so that everybody can work harmoniously toward a common goal.
Professionals who can benefit from using a PSA tool are:
- Business owners
- Finance staff
- Administrative staff
- Service desk personnel
- Service desk managers
- Technicians
- Project managers
- Sales and account management
A PSA solution should offer a wide variety of features so that you can automate and streamline a greater number of tasks. Here are a few of the core modules a PSA should have:
- Service desk and ticketing: The service desk feature is the top highlight of a PSA system since its quality has a direct impact on your customer relations. Ticketing, a core service desk function, helps technicians track the progress of IT requests raised by clients. The automated ticketing module in a PSA can prioritize tickets based on severity and complexity, so that technicians can take on business-critical challenges immediately. It should even be able to remediate simple issues without human intervention.
- management: Anybody working on a project should be able to access real-time updates and information since all project workflows and information are centralized. In this way, projects continue to move forward smoothly even when technicians with critical roles leave the company.
- Time, expense and service tracking: In a modern PSA system, time and cost tracking provides you with a complete picture of your actual versus planned expenditures, allowing you to stay on top of your spending and pivot your business accordingly. Your business can grow faster if you are in control of your costs.
- Quoting: You can use a quote to communicate the value of your services and products to clients and prospects and gain their approval more quickly.
- Billing and invoicing: Modern PSA systems eliminate the hassle of manually reconciling client data and give you precise details on each client account so you can facilitate accurate billing. PSA tools also accurately capture changes in costs when clients modify service plans midcycle. Having your services billed on time allows you to earn steady revenue and make better use of all your earnings. Billing accurately also boosts your MSP’s credibility.
- Reporting: Powerful reporting provides real-time insights and aligns your service desk with world-class standards. BMS by Kaseya offers out-of-the-box dashboards and reports to highlight metrics that matter.
- Pricing: Take into consideration the initial implementation cost, the integration cost, the migration cost, the per-user cost, the module cost, the cost of modifying configurations to meet future needs and so on before you make your decision.
- Migration and implementation: An effective migration strategy will help you avoid obstacles, minimize risks and give you more control over the process.
PSA integration is the ability of a PSA solution to interoperate seamlessly with several core business tools necessary to run an organization. MSPs can improve customer service, increase turnaround time on administrative tasks and better use their databases by integrating core tools. Integration also enables MSPs to switch between applications effortlessly, simplifying and streamlining their work, saving time and money.
BMS seamlessly integrates with your other core IT management applications and allows you to manage different workflows and processes from a single dashboard and minimize errors. Simplify billing by automatically creating and posting invoices from time entries and expense reports. Integration with accounting software like QuickBooks® and Xero® and open integration with major RMM and accounting systems are also available. Unlock your techs’ knowledge and efficiency with our deep IT Glue integration. With zero degrees of separation, your techs can find information faster and more accurately than ever before, achieving the highest levels of consistency and service for your customers.
Since Kaseya BMS also has the most affordable terms available, you can invest your savings back into your business for further growth and customer retention.


