Many businesses and MSPs are still reeling from the supply chain attack that took place in December 2020. Even U.S. government agencies, such as the Department of Justice (DOJ), weren’t spared as hackers breached their IT systems using the SolarWinds Orion app as the entry point. In the case of the DoJ, the hackers were able to access email accounts of some of its employees.
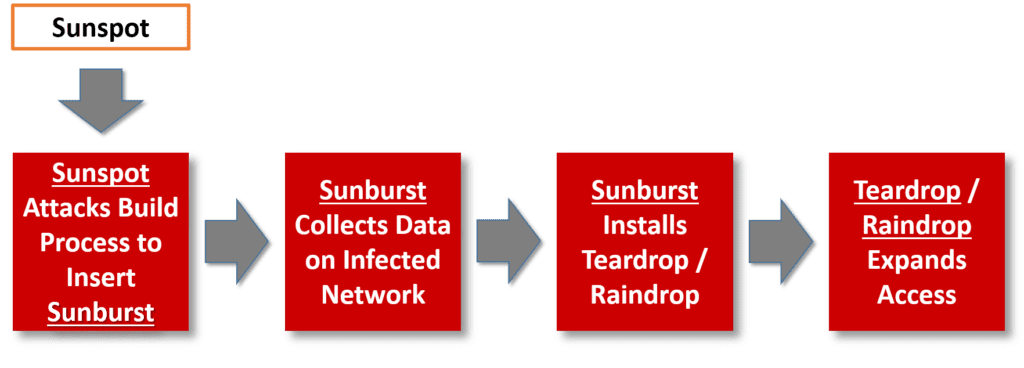
The latest information on this supply chain attack, as described in this ZDNet article, indicates that hackers used a total of four malware strains: Sunspot, Sunburst (Solorigate), Teardrop and Raindrop. These malware strains were used in a sophisticated sequence of escalated attacks. First, Sunspot was used to attack the vendor’s software build process and insert the Sunburst malware into the Orion software. The Sunburst malware collected data on infected networks and sent it to a remote server.
In cases where the attackers wanted to further escalate the attack, they used Sunburst to install either the Teardrop or Raindrop malware. Both are backdoors that the attackers used to “broaden their access inside a hacked IT network.” So, security teams must scan their IT environments for all four of these strains of malware.
Effective Tips To Better Protect Your Business
Based on its research of the attack, the security firm Cycode suggests six security measures your organization should take to reduce its exposure to risk.
Cycode recommends strengthening your infrastructure’s access controls with:
- Complete visibility and inventory of all assets – Any asset that is not monitored can become a vulnerability to your ecosystem.
- Multifactor authentication (MFA) – Passwords alone cannot protect accounts, especially ones that are as simple as “password123.” MFA provides an extra layer of protection, making it harder for hackers to access your systems.
- Auditing of systems – Get rid of default credentials on your systems and enforce strict password policies.
- Enforcing privilege policies – A privileged user has administrative access to all your critical systems. Managing and monitoring all privileged accounts is essential for better security.
Another security firm, Tempered Networks, suggests that a “zero trust” approach must be implemented to strengthen organizational security. This mechanism includes:
- Network microsegmentation – Zero trust network access (ZTNA) applies policies for what a user can access. With applications being separated in this architecture, admins can decide access permissions at a very granular level.
- Device verification and user authentication – Access is provided only when a user proves who they are and if they are secure. With multiple validations done, ZTNA allows access only to verified users.
How MSPs Can Protect Clients?
MSPs can take a proactive approach and provide security operation center (SOC) services such as:
Endpoint Security
MSPs can secure their customers’ endpoints with –
- Event log monitoring – Event log monitoring for all Windows and MacOS machines is crucial to track events across all devices from a unified console.
- Threat hunting – Proactively identifying security incidents before they have caused damage can keep your customers safe from major losses to their businesses.
- Intrusion detection – MSPs can set alerts to detect suspicious activities and barricade intruders from taking over other systems.
- Third-party, next-generation antivirus/antimalware (NGAV) – Integrating with NGAV solutions provides advanced threat detection on endpoints rather than simply looking for known malware signatures.
Network Security
MSPs can provide firewall and edge device log monitoring integrated with threat reputation services (TRS) and Whois and DNS lookup services.
TRS includes conducting frequent threat assessments against websites, files, domain names and other such entities to categorize the number of times these entities have been associated with malicious activity, based on observed past behavior and shared intelligence.
Cloud Security
The cloud security services mentioned below can be provided by MSPs to keep their clients’ cloud data safe.
- Microsoft 365 security event log monitoring
- Microsoft Office 365, Google G Suite and Salesforce Data Backup
- Azure Active Directory (AD) monitoring
- Microsoft 365 malicious logins and
- Azure Secure Score
While we may not yet know the extent of the Orion attack, organizations fear more is yet to come. During these uncertain times, it is essential for businesses to redouble their cybersecurity efforts.
Learn more about how you can enhance your security posture by attending our webinar “Boosting IT Security in 2021.” Register now!


